The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) refer to a comprehensive, far-reaching and people-centered set of universal and transformative goals that all countries of the world have agreed to achieve by the year 2030. In 2015, at the 70th United Nations (UN) General Assembly, member states unanimously adopted "Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development", which contains 17 goals and 169 targets based on people, the planet, prosperity, peace and partnership.
The SDGs are followed up and reviewed at the global, regional and national levels every year, based on data provided by each country. This data should have high-quality and reliability. In order to support the principle of inclusiveness such as "Leaving No One Behind", it is emphasized that all indicators are disaggregated by sex, age, income, disability, migration status, geographic location and other characteristics relevant in the national context.
Development of Global Indicator Framework
In accordance with the resolution, the global indicator framework was developed by the Inter-Agency and Expert Group on SDG Indicators (IAEG-SDGs), which consists of representatives of national statistical offices. The IAEG-SDGs conduct its work in an open, inclusive and transparent manner through the participation of various stakeholders. The indicator framework was agreed upon at the 48th session of United Nations Statistical Commission held in March 2017, and adopted thereafter by the General Assembly in July of the same year. According to the work plan, the indicator framework will be refined with minor things annually, and comprehensively reviewed in 2020 and 2025.
The first Comprehensive Review was held by the 51st UN Statistical Commission in March 2020. The IAEG-SDGs proposed 36 indicators to the existing framework in the form of replacements, deletions and additions. 231 indicators were approved through discussions among the Member States. In the future, the implementation of the SDGs will be monitored based on this framework.
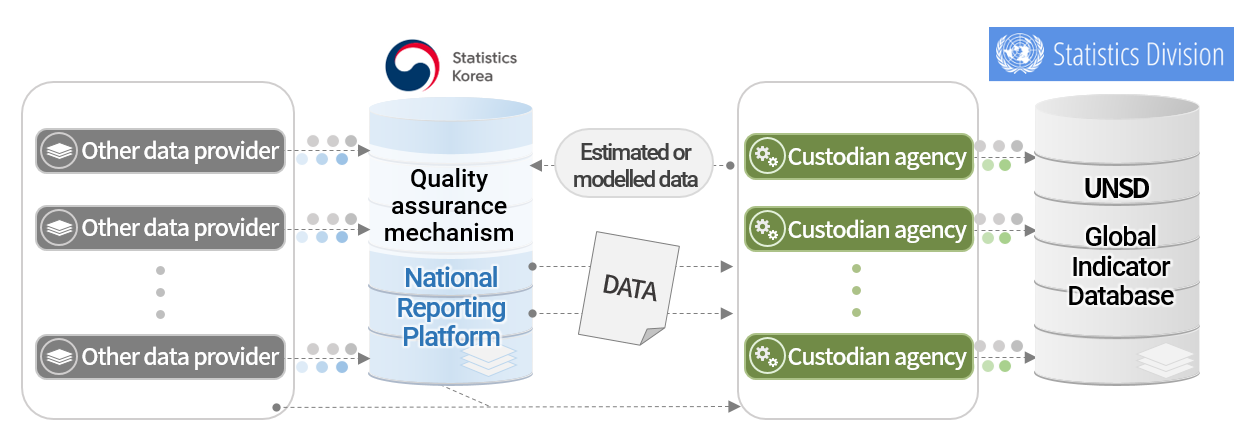
The United Nations Statistics Division released the Global SDG Indicators Database. The Database includes country level data as well as regional and global aggregates. Statistics Korea (KOSTAT) is a focal point for the SDG Indicators in the Republic of Korea, which is responsible for collecting and providing Korean data to the global community including the UN and international organizations. These data are produced by domestic statistical agencies and managed by the quality assurance system of KOSTAT. KOSTAT also reviews the Korean data estimated or modelled by international organizations. National data may be adjusted for international comparability or where data were missing.